Pregnancy brings a whirlwind of questions about diet and nutrition, and one common concern revolves around eating pork. Expectant mothers often wonder if indulging in this popular meat is safe for them and their developing baby. With various guidelines and recommendations, it’s essential to sift through the information to make informed choices.
Pork can be a delicious source of protein and essential nutrients, but it also carries potential risks if not handled or cooked properly. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy. By exploring the safety of pork consumption during this special time, expectant mothers can enjoy their meals with confidence while prioritizing their health and that of their little one.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Dietary Restrictions During Pregnancy
Pregnancy requires careful attention to dietary habits. Pregnant individuals face various dietary restrictions to ensure their health and that of their developing babies. Key guidelines recommend avoiding certain foods that pose risks, such as raw or undercooked meats, unpasteurized dairy, and some fish.
Risks of Consuming Pork
Consuming pork presents specific risks if preparation and cooking methods are inadequate. Pork may harbor parasites, like Trichinella spiralis, which can lead to trichinosis, a potentially serious infection. Thorough cooking eliminates this risk. Pork should reach an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) followed by a resting time of three minutes.
Nutritional Benefits of Cooked Pork
Cooked pork offers numerous nutritional benefits. It serves as an excellent source of protein, providing essential amino acids necessary for fetal growth. Pork also contains vital vitamins and minerals, such as B vitamins (including B12), iron, and zinc. These nutrients support both maternal health and fetal development.
Safe Consumption Practices
To enjoy pork safely during pregnancy, adhere to these practices:
- Select Quality Cuts: Choose lean cuts of pork to minimize fat intake.
- Avoid Processed Pork: Limit consumption of processed meats like bacon and deli meats, which may contain harmful additives.
- Practice Proper Hygiene: Wash hands, utensils, and surfaces thoroughly when preparing pork.
- Store Appropriately: Refrigerate raw pork at 40°F (4°C) or below and use it within one to two days.
Pregnant individuals can include pork in their diet by following these precautions, thus ensuring both safety and enjoyment without compromising health.
Nutritional Benefits of Pork
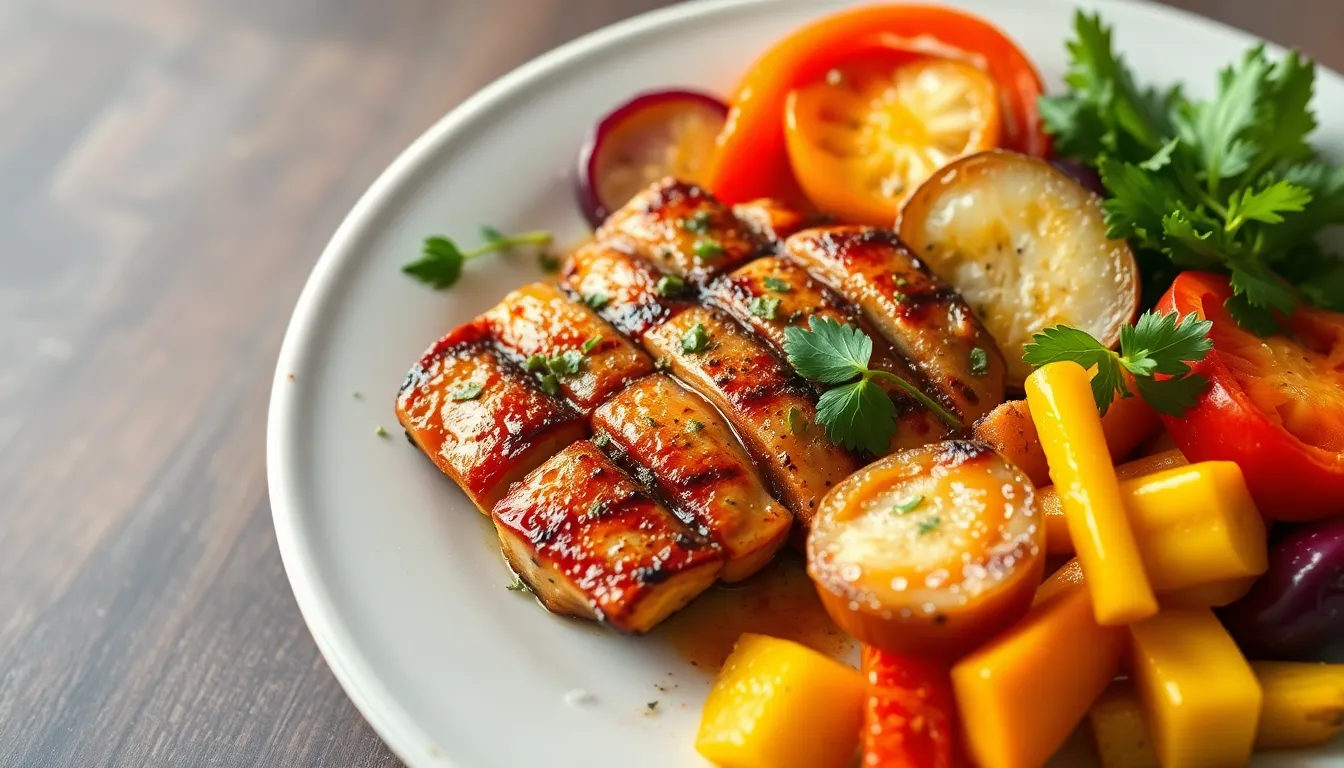
Pork offers various nutritional benefits essential for expectant mothers. It serves as a significant source of key vitamins and minerals that support both maternal and fetal health.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Pork contains essential vitamins and minerals, crucial for pregnancy.
- B Vitamins: Pork is rich in B vitamins, including B1 (thiamine), B3 (niacin), B6, and B12. These vitamins help maintain energy levels, support brain development, and contribute to the formation of red blood cells.
- Iron: Pork provides heme iron, which is more easily absorbed than non-heme iron from plant sources. Adequate iron intake can reduce the risk of anemia during pregnancy, ensuring sufficient oxygen delivery to the mother and fetus.
- Zinc: Zinc plays a vital role in cell division and immune function. Pork is an excellent source, helping to support the developing baby’s growth and the mother’s health.
Protein Source
Pork serves as a high-quality protein source, essential for healthy fetal development.
- Muscle Development: Protein is vital for building and repairing tissues. Consuming sufficient protein supports the growth of the placenta and fetal muscles.
- Satiety: Protein-rich foods can promote feelings of fullness, helping manage weight gain during pregnancy.
- Amino Acids: Pork contains all essential amino acids, crucial for the formation of proteins in the body, supporting both maternal and fetal health.
Risks Associated with Eating Pork While Pregnant
Pork consumption during pregnancy carries certain risks that expectant mothers should understand. Those risks mainly involve bacterial contamination and parasitic infections that can affect the health of both the mother and the developing baby.
Potential Bacterial Contamination
Eating undercooked or improperly handled pork can lead to bacterial contamination. Common pathogens include Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli. Salmonella can cause severe gastrointestinal distress and is associated with raw or undercooked pork. Listeria poses a higher risk during pregnancy, as it can lead to miscarriage or stillbirth. E. coli infections result from inadequate cooking and can cause severe abdominal cramps and diarrhea. Cooking pork to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) reduces the likelihood of bacterial infections.
Risk of Parasites
Parasites present another significant risk when eating pork during pregnancy. Trichinella spiralis, the parasite responsible for trichinosis, can lead to severe illness if pork is not cooked thoroughly. Symptoms of trichinosis include fever, muscle pain, and gastrointestinal upset. Cooking pork to the recommended internal temperature kills these parasites, making it safe for consumption. Additionally, ensuring proper food handling and hygiene practices can further mitigate the risk of parasitic infections.
Safe Practices for Consuming Pork
Pregnant women can safely consume pork with proper precautions. Following safe cooking methods and selecting quality products ensures optimal nutrition and minimizes health risks.
Proper Cooking Techniques
Cooking pork to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) effectively eliminates harmful pathogens. Using a meat thermometer guarantees accurate temperature readings. Ground pork should reach 160°F (71°C) to ensure safety. Resting pork for at least three minutes after cooking allows for continued cooking and enhances juiciness. Avoiding undercooked or raw pork is essential, as it can lead to infections like trichinosis and bacterial contamination.
Choosing Quality Products
Selecting high-quality cuts of pork reduces the risk of contamination and increases nutritional value. Opting for fresh, organic, or locally sourced pork ensures higher standards of animal welfare and food safety. Pregnant women should avoid processed meats like hot dogs, bacon, and deli meats due to additives and potential listeria exposure. Checking labels for additives and preservatives helps in making healthier choices. Proper storage, including refrigeration and freezing, maximizes the freshness and safety of pork products.
Alternatives to Pork
Pregnant women seeking alternatives to pork can find various protein-rich foods that provide essential nutrients.
- Chicken: Chicken offers lean protein, B vitamins, iron, and zinc. It should be cooked thoroughly to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
- Turkey: Turkey serves as a low-fat option with similar nutritional benefits as chicken. Cooked turkey also enhances iron and zinc intake.
- Fish: Safe seafood options, such as salmon or sardines, provide omega-3 fatty acids essential for fetal brain development. Opt for well-cooked fish to minimize contamination risks.
- Beef: Lean cuts of beef supply high-quality protein, iron, and B vitamins. Proper cooking to at least 145°F (63°C) ensures safety before consumption.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent plant-based protein sources rich in fiber, iron, and folate. They offer nutritious alternatives for pregnant women who prefer vegetarian diets.
- Tofu: Tofu contains protein and important minerals, such as calcium and iron. It is versatile in cooking and suitable for pregnant women seeking vegetarian options.
- Eggs: Eggs provide protein, choline, and various vitamins. They must be cooked until both the yolk and white are firm to ensure safety.
Incorporating these alternatives can support a well-rounded diet while avoiding potential risks associated with pork consumption during pregnancy.
Expectant mothers can enjoy pork as part of a balanced diet when proper precautions are taken. By ensuring that pork is cooked thoroughly and handled safely, they can minimize the risks associated with bacterial contamination and parasitic infections. The nutritional benefits of well-prepared pork can contribute significantly to both maternal health and fetal development.
It’s crucial to prioritize quality cuts and avoid processed meats to further reduce potential hazards. Alongside pork, incorporating a variety of protein-rich alternatives can help maintain a nutritious diet during pregnancy. With informed choices and careful preparation, pregnant women can safely include pork in their meals while supporting their health and that of their baby.



